Clearing goods through Saudi Customs is a structured yet complex process that requires strict adherence to regulations set by the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA). Whether you’re an importer, exporter, or logistics provider, understanding the key steps ensures smooth clearance, avoids costly delays, and minimizes penalties.
Saudi Arabia has been actively modernizing its customs procedures to enhance trade efficiency. Recent reforms include digital transformation initiatives such as the FASAH platform, mandatory Advance Cargo Declaration (ACD), and AI-driven risk assessment systems for faster processing. Additionally, certain sectors—such as renewable energy and healthcare—benefit from reduced tariffs in line with Vision 2030 economic goals.
Non-compliance, however, can lead to shipment holds, fines, or even confiscation of goods. This guide breaks down the essential steps for Saudi customs clearance, including the latest 2025 amendments, required documents, duty calculations, and common pitfalls to avoid. Stay informed to ensure seamless cross-border trade in the Kingdom.
Pre-Arrival Preparation: Setting the Foundation for Smooth Saudi Custom Clearance
Before your shipment reaches Saudi ports, proper preparation is crucial to avoid delays, fines, or even confiscation. Saudi Arabia’s customs authority, ZATCA (Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority), has implemented digital reforms to streamline trade—but compliance is mandatory. Here’s what you need to do before your goods arrive:
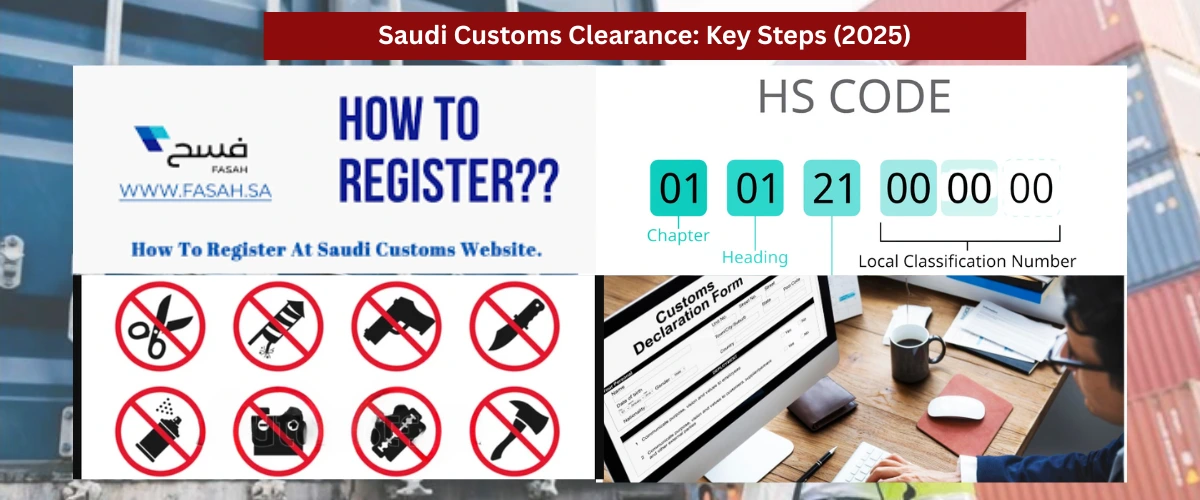
1. Register as an Importer/Exporter on FASAH
All businesses importing into Saudi Arabia must register on ZATCA’s FASAH platform (Facilitate Sea, Air, and Highway Customs Clearance). This digital system connects traders with customs authorities for faster processing.
Steps to Register:
- Create an account on FASAH.
- Submit company documents (Commercial Registration, VAT certificate).
- Obtain an Importer/Exporter Code (IEC).
- New in 2025: Individual importers can now register for small-scale shipments.
Non-compliance Risk: Unregistered shipments may be held at customs, leading to storage fees.
2. Correct HS Code Classification
Saudi Arabia follows the Harmonized System (HS) Code for customs tariffs. Misclassification can result in wrong duty payments or shipment rejection.
How to Find the Right HS Code?
- Use ZATCA’s updated Customs Tariff Guide (2025).
- Consult a customs broker for complex items (e.g., machinery, chemicals).
3. Check Prohibited & Restricted Items (2025 Updates)
Saudi customs strictly bans certain goods, while others require special permits.
Prohibited Items (2025):
- Drones (without Saudi General Authority of Civil Aviation approval).
- Gambling equipment, narcotics, and religiously offensive materials.
- Used or refurbished electronics (unless approved by SASO).
Restricted Items (Need Permits):
- Pharmaceuticals (SFDA approval required).
- Food products (must meet Saudi Food & Drug Authority standards).
- Wireless devices (requires CITC certification).
4. Submit Advance Cargo Declaration (ACD) – Mandatory!
Since 2024, Saudi customs requires an Advance Cargo Declaration (ACD) for all shipments before arrival.
Key Rules for ACD:
- Submit at least 24 hours before shipment departure (sea/air).
- Include: HS Code, invoice value, consignee details.
- Failure to submit = Customs hold + penalties (up to SAR 10,000).
Required Documents for Saudi Customs Clearance (2025 Update)
Submitting the correct documentation is the most critical step in Saudi customs clearance. Missing or incorrect paperwork can lead to delays, fines, or even shipment rejection. Here’s the complete checklist of required documents, including the latest digital submission rules:

1. Commercial Invoice (Attested)
- Must include: Exporter/Importer details, product description, quantity, value (in SAR or USD), and HS Code.
- New Rule (2025): Invoices exceeding SAR 10,000 must be attested by the Saudi Chamber of Commerce or a Saudi embassy/consulate.
- Digital Option: E-invoices can now be submitted via ZATCA’s portal for faster processing.
2. Bill of Lading (Sea) or Air Waybill (Air Freight)
- Must match the commercial invoice details exactly.
- House vs. Master B/L: If using a freight forwarder, ensure both are submitted.
- Electronic Submission: Accepted through FASAH for paperless clearance.
3. Certificate of Origin
- Required to prove where goods were manufactured.
- GCC Goods: If products are from a GCC country, the certificate must be GCC-approved for preferential tariffs.
- Non-GCC Goods: Must be notarized by the local chamber of commerce and Saudi embassy.
4. Import License (For Restricted Goods)
- Medical/Pharmaceuticals: Requires SFDA (Saudi Food & Drug Authority) approval.
- Chemicals/Industrial Goods: Needs SASO (Saudi Standards) certification.
- Electronics/Wireless Devices: Must have CITC (Communications Authority) clearance.
5. Other Supporting Documents
- Packing List (Detailed weight, dimensions, and packaging type).
- Insurance Certificate (For high-value shipments).
- SASO/SABER Certificate (For regulated products).
Latest Update (2025): Fully Digital Submissions via ZATCA
- All documents can now be uploaded electronically through ZATCA’s FASAH platform.
- No physical copies required unless customs requests an inspection.
- Benefit: Reduces clearance time from 3-5 days to under 24 hours for compliant shipments.
Customs Declaration & Submission: How to File for Faster Clearance
Once your documents are ready, the next step is submitting the customs declaration. Saudi Arabia has introduced major digital upgrades in 2024 to speed up this process.
1. Online Submission via ZATCA’s Single Window (FASAH)
- All declarations must be filed electronically through FASAH.
- Steps to Submit:
- Log in to your FASAH trader account.
- Enter shipment details (HS Code, value, weight).
- Upload scanned copies of required documents.
- Pay estimated duties/VAT online.
- Receive a tracking number for real-time updates.
2. New Feature: AI-Powered Risk Assessment System
- Saudi Customs now uses an automated risk assessment system to categorize shipments:
- Green Channel (Low Risk): Cleared instantly (no inspection).
- Yellow Channel (Medium Risk): Random document check.
- Red Channel (High Risk): Physical inspection required.
- Benefit: Over 60% of shipments now clear within 2 hours under the Green Channel.
3. Customs Duties & VAT Calculation
- Basic Customs Duty: Ranges from 0% to 20% (depending on HS Code).
- VAT: 15% (Standard rate since 2024).
- Exceptions:
- GCC Goods: 0% duty under the GCC Common Customs Law.
- Renewable Energy Equipment: 5% duty reduction (Vision 2030 incentive).
4. Latest Update: Reduced Tariffs on Key Sectors
- Solar Panels & EVs: Now 5% duty (down from 12%).
- Medical Equipment: 0% duty for approved hospitals/clinics.
- Raw Industrial Materials: 2% duty (to support local manufacturing).
Inspection & Examination at Saudi ports
Even with perfect documentation, your shipment may undergo customs inspection—either randomly or due to risk assessment flags. Here’s how Saudi Arabia’s process works in 2025:

1. Risk-Based Inspection System
- Green Lane (Low Risk): No inspection (auto-clearance in hours).
- Yellow Lane (Medium Risk): Document verification (1-2 days).
- Red Lane (High Risk): Physical inspection (3+ days, extra fees apply).
2. Special Cases Requiring Extra Certification
- Food & Pharmaceuticals: Must pass SFDA (Saudi Food & Drug Authority) checks.
- Electronics & Appliances: Need SASO/SABER certification for safety compliance.
- Chemicals/Industrial Goods: Require Royal Commission for Jubail & Yanbu approval.
3. New E-Invoicing Rule (Phase 2 for B2B)
- Since 2024, all B2B invoices must comply with ZATCA’s e-invoicing (FATOORAH).
- Non-compliant invoices lead to SAR 5,000+ fines.
Payment & Release: Final Steps to Free Your Goods
1. Payment Methods
- Online: Via SADAD (government payment system) or bank transfer.
- Port Cashier: Only for small shipments (under SAR 10,000).
2. Customs Duty Exemptions
- GCC-Made Goods: 0% duty under GCC trade agreements.
- Diplomatic Shipments: Exempt with proper embassy documentation.
3. Penalty Updates
- Late duty payments incur 5% monthly interest.
- Repeated delays may lead to importer blacklisting.
Post-Clearance: Last-Mile Logistics & Dispute Handling
1. Storage & Delivery Options
- Bonded Warehouses: Store goods duty-free for up to 90 days.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Must use Saudi Post or approved logistics firms.
2. Dispute Resolution
- Appeals must be filed within 30 days via ZATCA’s portal.
- Submit evidence (invoices, photos) for case review.
Streamline Your Saudi Customs Clearance with Expert Help
Navigating Saudi Arabia’s customs clearance process can be complex—especially with frequent regulatory updates like mandatory e-invoicing, risk-based inspections, and stricter penalty enforcement. One missing document or incorrect HS code can lead to costly delays, storage fees, or even shipment seizures.
By following the key steps outlined in this guide—pre-arrival preparation, accurate documentation, digital submissions via FASAH, and compliance with SASO/SFDA rules—you can minimize risks and ensure faster clearance. However, for high-value, time-sensitive, or regulated goods, partnering with a licensed customs clearance specialist is the safest way to avoid pitfalls.
Let Radhi Custom Clearance Co. Handle Your Saudi Shipments!
Why Struggle with Customs Delays? Trust Radhi Custom Clearance Co.—Saudi Arabia’s leading customs brokerage firm—to manage your imports/exports hassle-free.Don’t let customs delays hurt your business—partner with professionals. Contact Now!

Add a Comment